Qingdao Energy Research Institute has developed a high-performance gel polymer electrolyte for magnesium batteries
As a low-cost, high-security energy storage technology, magnesium secondary batteries are attracting the attention of researchers at home and abroad. The US Department of Energy ’s Renewable Energy Laboratory, Japan ’s Toyota Group, and the European Union ’s “Prospect 2020†scientific research plan are all actively deploying magnesium battery research and development projects, which shows their importance. Among many alkali metal and alkaline earth metal anodes (lithium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, zinc), magnesium metal anodes are not easy to grow dendrites, high volume specific capacity (3833mAh / cm3, lithium metal is only 2036mAh / cm3), High reserves (fifth content in the earth's crust elements), low cost (only 1 / 30th of lithium metal) and many other competitive advantages. However, the magnesium electrolyte that can effectively deposit and dissolve magnesium has been restricting the practical development process of magnesium batteries. Although researchers have developed some organic liquid electrolytes with excellent performance for more than ten years, liquid electrolytes have always been able to get rid of the shortcomings of volatility and flammability. Compared with liquid electrolytes, polymer electrolytes have the advantages of higher safety, prevention of internal short circuits, no electrolyte leakage, easy assembly of batteries and structural flexibility, but there are few reports on the application of polymer electrolytes in magnesium batteries .
Based on the above research background, relying on the in-situ cross-linking reaction of magnesium borohydride and polytetrahydrofuran-terminated hydroxyl groups, the Qingdao Energy Storage Industry Technology Research Institute built by the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Processes of the Chinese Academy of Sciences built a A gel polymer electrolyte system in which magnesium is dissolved is reversibly deposited. The gel electrolyte exhibited a high magnesium ion migration number (0.73) and a high room temperature ion conductivity (4.76 × 10-4 S / cm). The Mo6S8 / Mg battery equipped with the gel electrolyte system can not only work normally in a wide temperature range (-20-60 ℃), but also exhibit excellent safety performance. This in-situ cross-linking method provides a very promising strategy for the further development of polymer electrolytes for magnesium batteries. Related results were published in "Advanced Materials" (Advanced Materials), the first author of the paper is Qingdao Energy Institute doctoral student Duo Bing.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation Outstanding Youth Fund Project, National Key R & D Program and Qingdao Science and Technology Project Fund.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the structure and application fields of gel polymer electrolyte
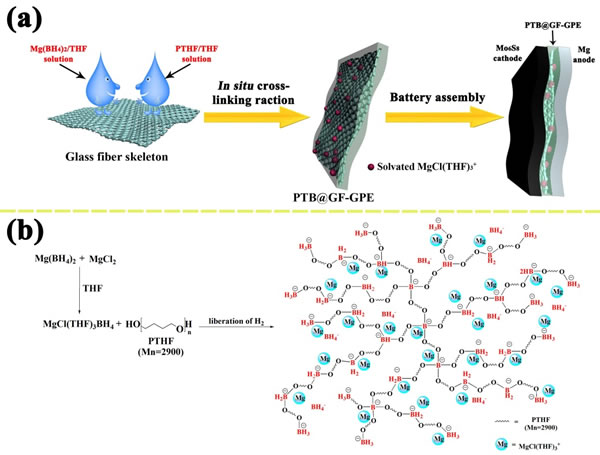
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of in-situ cross-linking reaction between magnesium borohydride and polytetrahydrofuran terminal hydroxyl groups
NSK deep groove ball bearings,NSK tapered roller bearings,NSK angular contact ball bearings,NSK spherical roller bearings,NSK cylindrical roller bearings
Shanghai Yi Kai Cheng bearing Co., LTD , https://www.ykcbearing.com