Progress in the Research on High-Efficiency Catalysis of Hydrogen Peroxide Electrosynthesis of Nanocarbon Materials at Institute of Metals
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a green, renewable, and environmentally friendly oxidant that is widely used in environmental remediation, fine chemicals, and electronics industries. The industrial production of hydrogen peroxide mainly relies on the "anthraquinone method" which uses hydrogen and oxygen as raw materials, but this method has the problems of high energy consumption, difficulty in the transfer and storage of raw materials and products, and serious safety hazards. The new method of preparing hydrogen peroxide through the electrochemical oxygen reduction route has received attention as a potential alternative route. At present, the catalysts used in the process of electrochemical oxygen reduction to prepare hydrogen peroxide are mainly noble metal materials (Pd, Au, Ag, Pt-Hg, etc.), but their limited reserves and high prices make it difficult to meet the green, environmental protection and sustainable development of modern engineering. Demand. Nano-carbon materials are expected to be used as a substitute for precious metal catalysts and used in electrochemical oxygen reduction reactions.
The Energy Catalytic Materials Group of the Joint Research Department of the Shenyang National Research Center for Materials Science, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences is devoted to the development of carbon catalytic reaction processes and novel carbon catalytic reaction systems. Recent progress has been made in the field of nano-carbon materials for the efficient catalytic hydrogen peroxide electrosynthesis. The research team found that the selectivity of the two-electron oxygen reduction reaction is linearly correlated with the content of carbonyl and carboxyl groups on the surface of the carbon material by correlating the chemical structure of the surface of a typical carbon material and its catalytic activity for the electrochemical reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. The intrinsic activity is more than 5 times that of the carbonyl functional group. The carboxyl functional group on the surface of the carbon material is the main active center for the electrochemical reduction of oxygen to produce hydrogen peroxide. The above research results of carbon-catalyzed oxygen electrochemical reduction active center and reaction kinetics also indicate that the selectivity of the oxygen reduction reaction mainly depends on the binding ability between the hydrogen peroxide and the carboxyl functional group. If the hydrogen peroxide generated by the two-electron oxygen reduction process on the carboxyl active site on the surface of the carbon material cannot be desorbed in time, it will be easily reduced to produce a four-electron reaction to generate water, so how to ensure the timely desorption of hydrogen peroxide on the active center Is the key to improve its selectivity and yield.
Based on the conclusions of the above reaction process and mechanism analysis, Dr. Qi Wei of the research team collaborated with Professor Guo Shaojun of Peking University and Xie Zailai of Fuzhou University to propose the use of interface engineering methods and reaction kinetics to control the choice of carbon-catalyzed electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction Research ideas. The specific method is to use the electrostatic interaction of a cationic surfactant (such as trimethyl cetyl ammonium bromide) and a carboxyl group to reduce the interaction between the carboxyl functional group on the surface of the carbon material and the dielectron oxygen reduction product HO2- to prevent it It is further reduced to achieve a highly selective electrosynthesis process of hydrogen peroxide. This carbon / surfactant composite catalytic material system exhibits the highest reported hydrogen peroxide selectivity (> 96%), the widest overpotential window (> 0.8V) and considerable stability (> 10h) . Based on the excellent catalytic performance of the nano-carbon / surfactant composite electrode material in the hydrogen peroxide electrosynthesis reaction, the entire reaction system has the characteristics of low energy consumption, greenness, sustainability and good stability. This research is of guiding significance for the design and development of electrosynthetic hydrogen peroxide compound systems with high yield, high stability and low cost with practical application prospects.
Related achievements were published in Journal of Colloid and Interface Science and Chem. Related research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province and the Shenyang National Research Center for Materials Science.
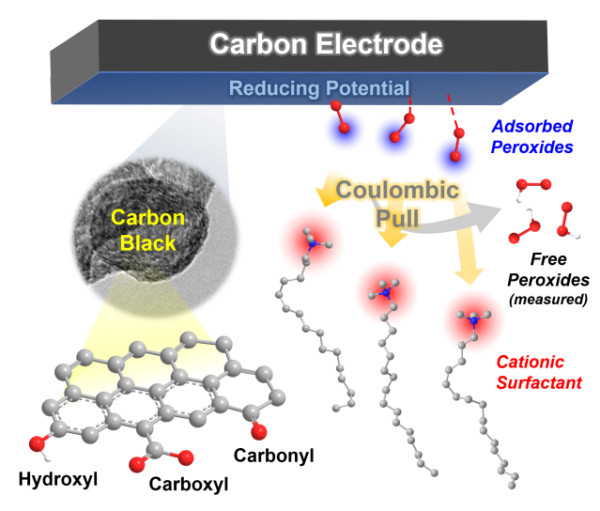
Schematic diagram of the promotion effect of carbon / surfactant system catalyzing oxygen reduction reaction with high selectivity to generate hydrogen peroxide
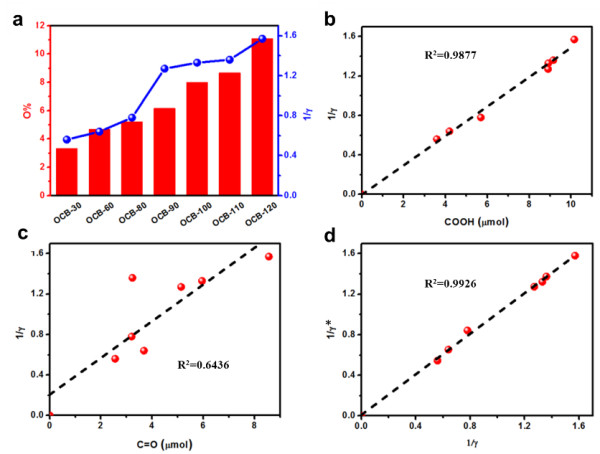
The relationship between the two-electron selectivity of the oxygen reduction reaction and the number of oxygen-containing functional groups (-COOH, C = O) on the surface of the carbon material: comparison of kinetic fitting and experimental results
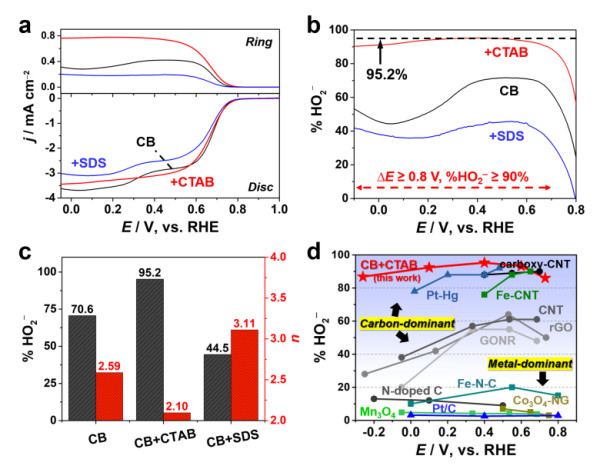
Comparison of hydrogen peroxide selectivity and potential window width of different electrocatalyst systems: the advantages of carbon / surfactant systems.
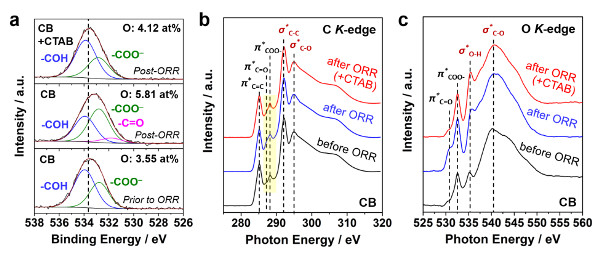
Chemical composition and structure of the carbon / surfactant system before and after the reaction: XPS O1s spectrum and K-edge spectrum of NEXAFS C / O
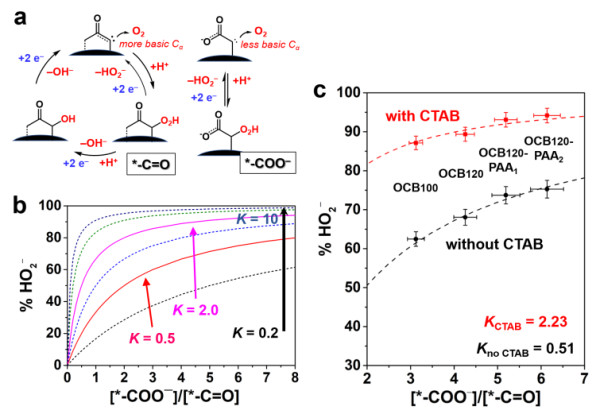
Carbon / Surfactant System Catalyzed Oxygen Electrochemical Reduction Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Analysis: Surfactant Promotes Hydrogen Peroxide Desorption
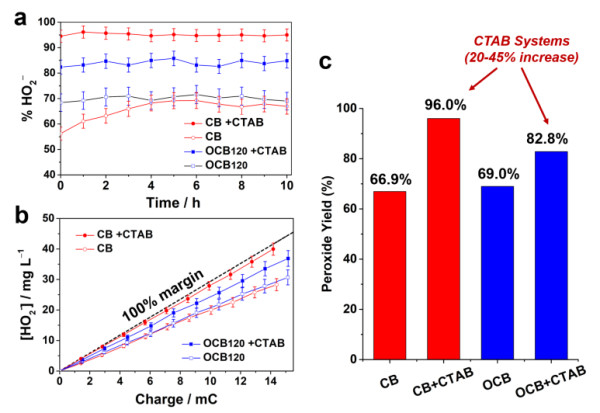
Carbon / surfactant system catalyzes the electrochemical reduction of oxygen to produce hydrogen peroxide with high selectivity: high efficiency and long-term stability
Dozer Parts,Bulldozer Spare Parts,Caterpillar Dozer Parts,Aftermarket Dozer Parts
JINING SHANTE SONGZHENG CONSTRUCTION MACHINERY CO.LTD , https://www.sdkomatsuexcavatorparts.com